Introduction
The use of fake driver’s licenses is a serious offense that undermines the safety and integrity of road – related systems. Law enforcement agencies are constantly on the lookout for individuals using these counterfeit documents, and they employ a variety of techniques and strategies to catch them.
Visual Inspection
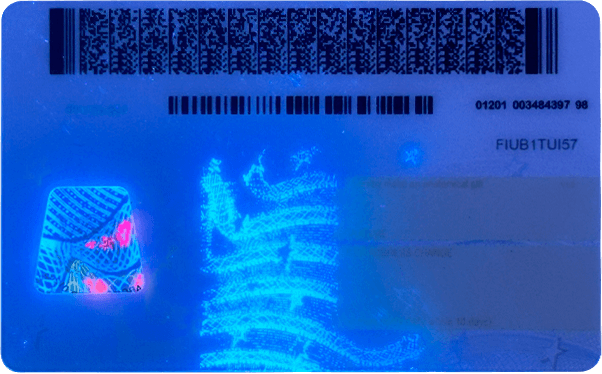
One of the first lines of defense for law enforcement is visual inspection. When an officer requests a driver’s license during a traffic stop or other encounter, they start by carefully examining the physical appearance of the license. Genuine driver’s licenses have specific design features that are difficult to replicate perfectly. For example, most real licenses have holograms, micro – printing, and color – shifting inks. Holograms are three – dimensional images that are embedded in the license and can only be replicated with advanced technology. Micro – printing involves tiny text that is almost invisible to the naked eye but can be easily detected under magnification. If an officer notices that the hologram is blurry, the micro – printing is missing or incorrect, or the color – shifting inks do not change as expected, it could be a sign of a fake license.
Another aspect of visual inspection is looking at the overall quality of the printing and the material. Real driver’s licenses are printed on high – quality plastic or paper with sharp, clear text and images. A fake license may have smudged text, pixelated photos, or a flimsy material that feels different from a genuine one. Additionally, the font used on the license should match the official font used by the issuing authority. If the font looks off or inconsistent, it can raise suspicion.
Database Checks
Law enforcement also relies heavily on database checks. When an officer has a driver’s license in hand, they can run the license number through various databases. These databases are maintained by the Department of Motor Vehicles (DMV) and other relevant agencies. The first check is usually to verify that the license number is valid and associated with the person presenting it. If the license number does not exist in the database or is associated with a different individual, it is a clear indication of a fake license.

Furthermore, the databases can provide additional information such as the date of issue, expiration date, and any restrictions on the license. If the information on the license does not match what is in the database, it is a red flag. For example, if the license indicates an expiration date that is earlier than what is recorded in the database, or if there are additional restrictions on the database record that are not shown on the license, it could mean that the license is fake. Law enforcement can also cross – reference the license with other databases, such as criminal records databases, to see if the individual has a history of fraud or other related offenses.
Technology – Based Detection
In today’s digital age, technology plays a crucial role in catching fake driver’s license users. Many law enforcement agencies are equipped with mobile devices that can scan driver’s licenses. These scanners can read the magnetic stripe or the barcode on the license, which contains encoded information about the license holder. The scanner can then quickly verify the authenticity of the license by comparing the encoded information with the information on the face of the license and the data in the relevant databases. If there are any discrepancies, the scanner can alert the officer.
Another technological advancement is the use of facial recognition technology. Some law enforcement agencies are integrating facial recognition software into their systems. When an officer scans a driver’s license, the software can compare the photo on the license with a live – scan of the individual’s face. If there is a significant mismatch between the two, it can be a sign of a fake license or identity theft. However, the use of facial recognition technology also raises privacy concerns, and its implementation is often subject to strict legal regulations.
Inter – Agency Cooperation
Law enforcement agencies do not work in isolation when it comes to catching fake driver’s license users. There is often extensive inter – agency cooperation. Local police departments, state troopers, and federal agencies such as the Department of Homeland Security may collaborate on investigations. For example, if a local police officer suspects a fake driver’s license and discovers that it may be part of a larger counterfeiting operation, they can share the information with state or federal agencies. These agencies may have more resources and expertise in dealing with organized crime related to fake documents.
Inter – agency cooperation also involves sharing intelligence and data. Different agencies may have access to different databases or sources of information. By sharing this information, they can build a more comprehensive picture of the fake driver’s license problem. For instance, if one agency has identified a particular group or individual involved in manufacturing fake licenses, they can share this information with other agencies so that they can be on the lookout for these specific fake licenses.
Common Problems and Solutions
- Problem: Subtle Forgeries
Some fake driver’s licenses are very well – made, with only subtle differences from the real ones. This can make visual inspection difficult, as the forgeries may be able to replicate many of the design features to a certain extent.
Solution: Law enforcement officers need to receive regular and in – depth training on the latest design features of driver’s licenses and the techniques used by forgers. They should also be provided with high – quality magnification tools and other inspection aids to help them detect these subtle differences. Additionally, technology – based detection methods can be more effective in such cases, as they can analyze the license in more detail than a human eye.
- Problem: Database Errors
There may be errors in the databases used for verification. For example, a valid license number may not be correctly recorded in the system, or there may be glitches in the database that cause false alarms.
Solution: Regular database maintenance and quality control are essential. Databases should be updated frequently to ensure the accuracy of the information. Additionally, law enforcement agencies should have procedures in place to handle database errors. When an officer encounters a situation where the database information seems inconsistent, they should be able to double – check with other sources or contact the relevant database administrators for clarification.
- Problem: Privacy Concerns with Technology
As mentioned earlier, the use of technology such as facial recognition raises privacy concerns. There is a risk of misusing personal data or making false identifications based on inaccurate technology.
Solution: Law enforcement agencies should operate within strict legal frameworks when using such technology. They should obtain proper authorization and follow established protocols for data collection, storage, and use. Additionally, technology providers should be held accountable for the accuracy of their systems. Regular audits and independent evaluations of the technology can help ensure that it is used fairly and accurately.
- Problem: Lack of Inter – Agency Coordination
In some cases, there may be a lack of effective coordination between different law enforcement agencies. This can lead to missed opportunities in catching fake driver’s license users and in breaking up counterfeiting operations.
Solution: Establishing clear communication channels and protocols for inter – agency cooperation is crucial. There should be regular meetings and information – sharing sessions between different agencies. Additionally, joint task forces can be formed to specifically target fake driver’s license issues. These task forces can bring together the expertise and resources of multiple agencies to more effectively combat the problem.
- Problem: Overwhelmed Resources
Law enforcement agencies may be overwhelmed with the number of cases related to fake driver’s licenses, especially in areas with high levels of fraud. This can lead to delays in investigations and a backlog of cases.
Solution: Allocating sufficient resources, both in terms of personnel and technology, is important. Agencies can also prioritize cases based on the severity of the offense and the potential impact on public safety. Additionally, community – based initiatives can be launched to raise awareness about the dangers of using fake driver’s licenses, which may help reduce the overall number of cases in the long run.
Fake ID Pricing
unit price: $109
| Order Quantity | Price Per Card |
|---|---|
| 2-3 | $89 |
| 4-9 | $69 |
| 10+ | $66 |